A smarter way to Design & Build
Let Cadnetics be the extension of your team. Get the reliable, on-demand support and cutting-edge technology you need to stay under budget and ahead of schedule.
Our core Services
Reality Capture
Design Support
Virtual Construction
Visualization
A seamless extension of your team
Complete solution
With our comprehensive service offerings, there’s no need to patchwork together multiple vendors to get the job done. We offer a complete, all-in-one solution that can be executed seamlessly from start to finish.
Industry-leading technology
Get access to the latest technology and skills without needing to invest in expensive equipment or specialized talent in-house. With our scalable solutions, pay for only what you need, and nothing more.
Flexible workflows
With our adaptable solutions, we fill the gaps in your projects and simplify your life. We offer on-demand support that fits seamlessly into YOUR workflow, not ours.
Reliable support
We understand how stressful tight deadlines can be and how much pressure you’re under, because we’ve lived it. We’ll go above and beyond to get your project done on time and on budget, period.
A few of our Happy clients
Expertise you can depend on
8000+
Successful projects completed
2000+
Happy clients served
30
Years in business
Pittsburgh roots. Nationwide impact.
We are proud to be forged in the "Steel City," the backbone of the building and construction industry in America. It is a hub for entrepreneurship, technology, ingenuity, and industrial force. As we have expanded our operations nationwide, we continue to hold these values close to our hearts.
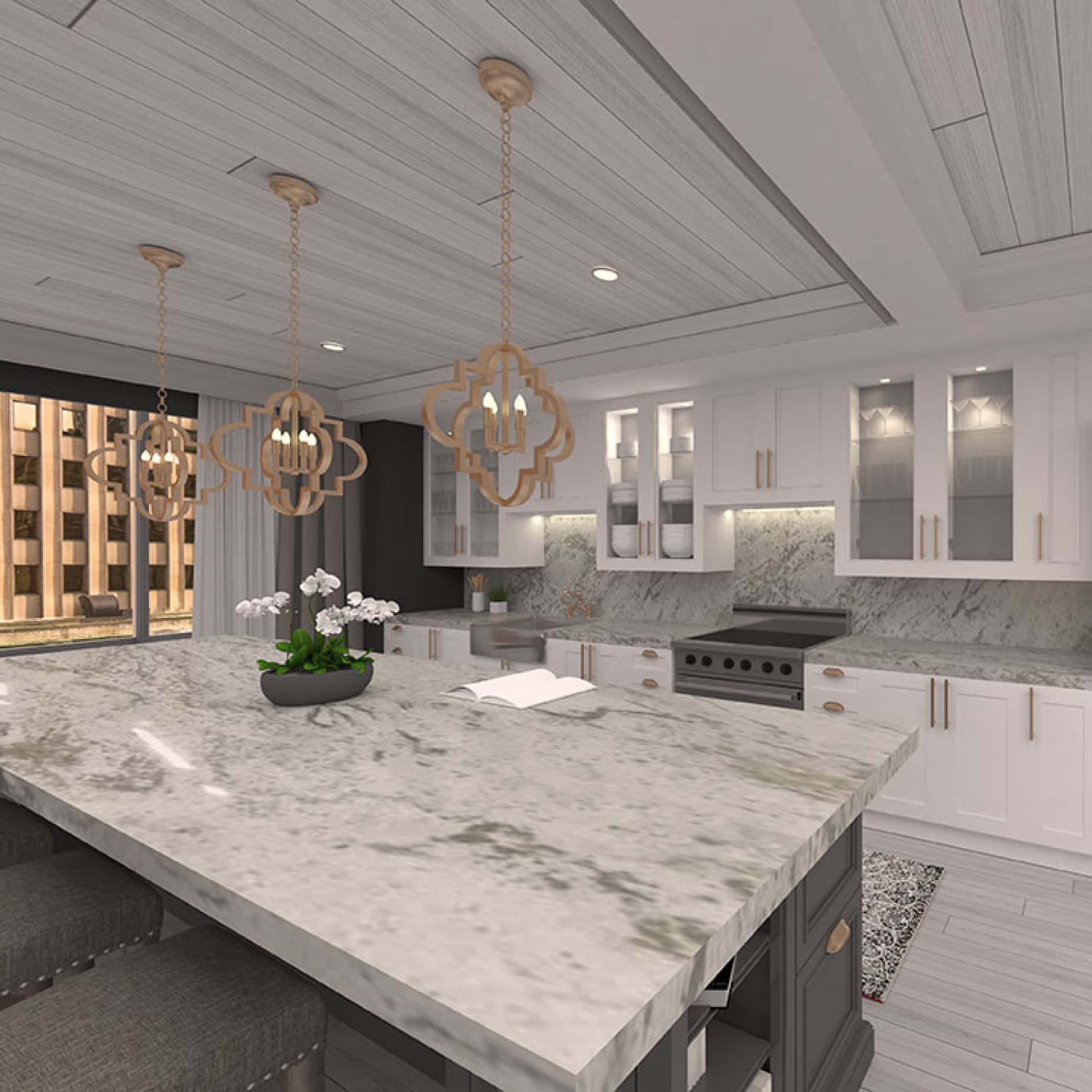
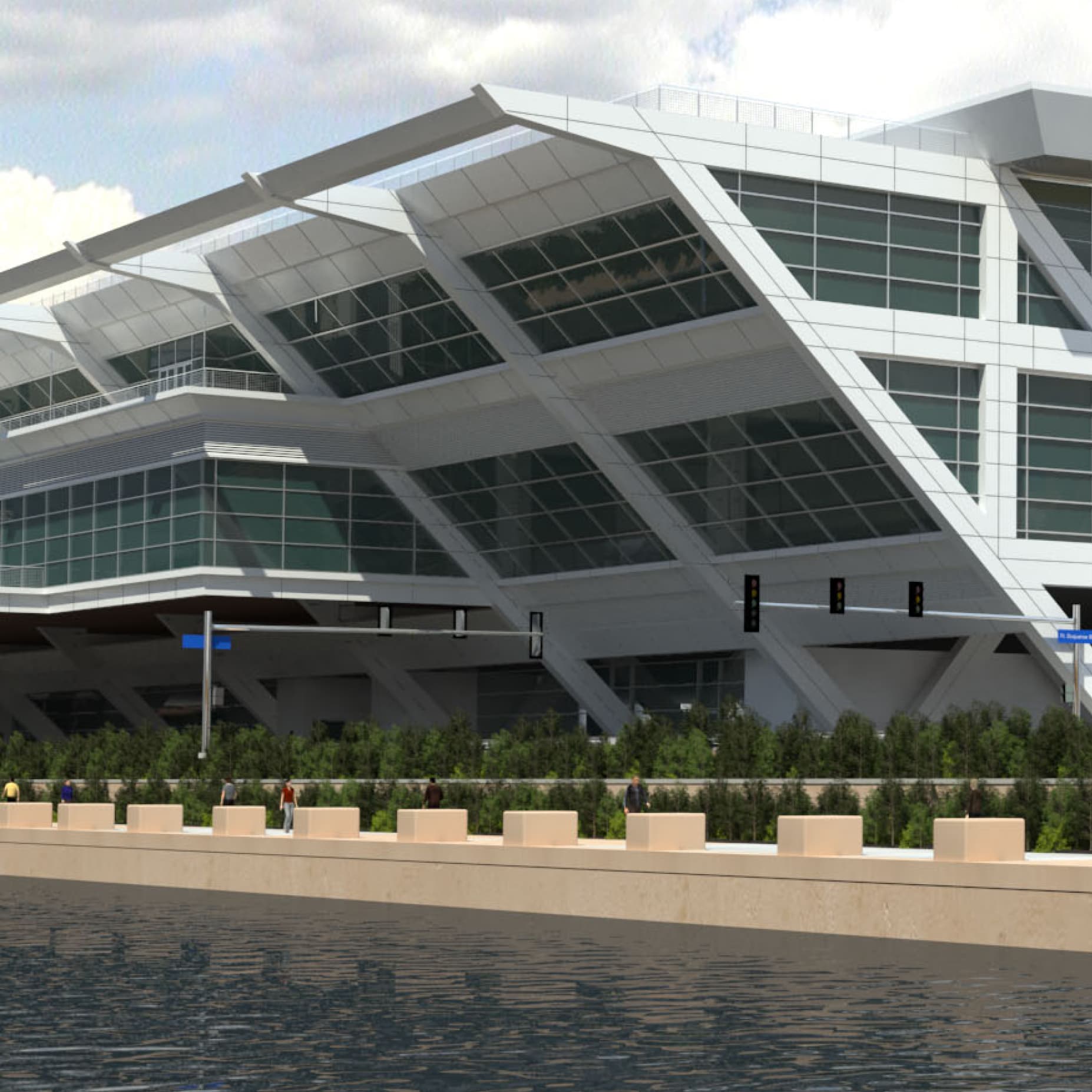
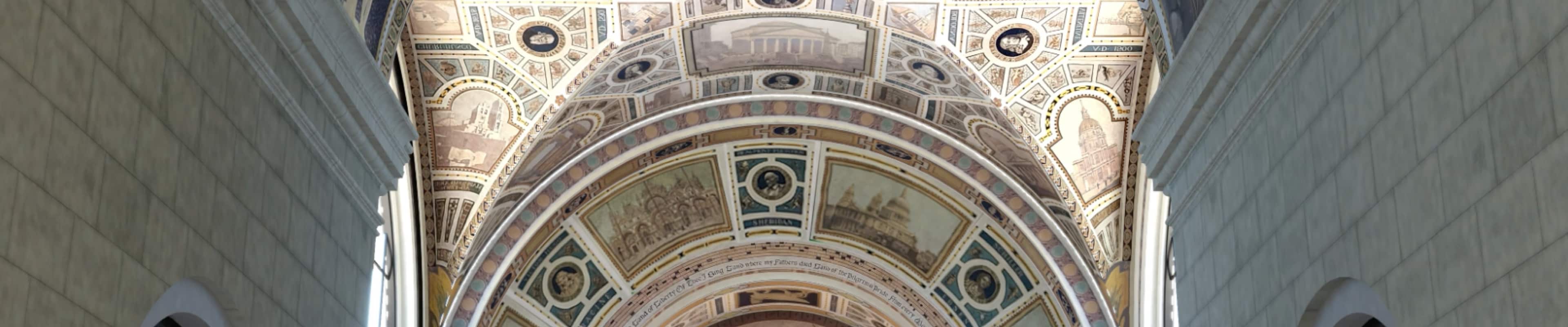
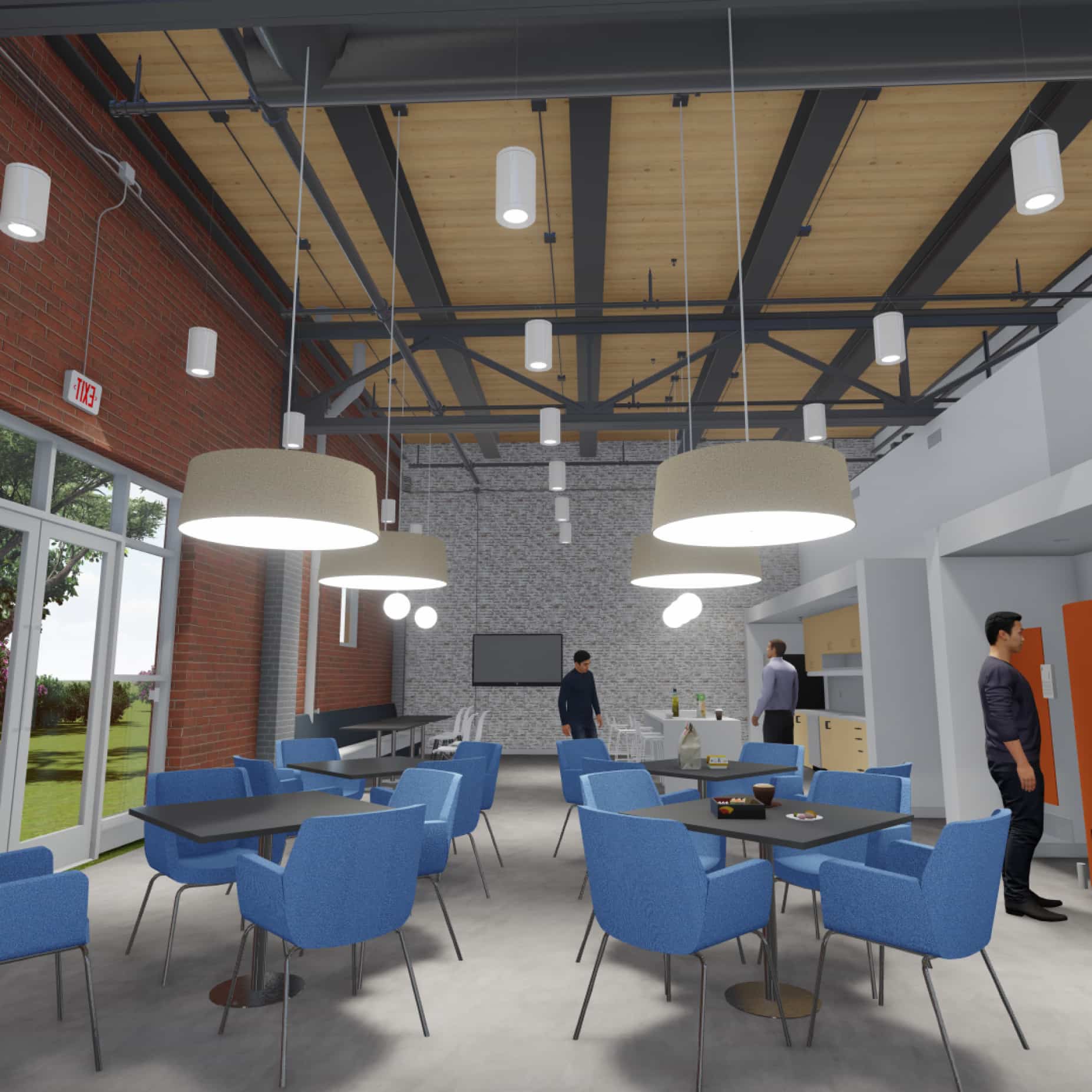
Select works we're proud of
Connected with the AEC Industry
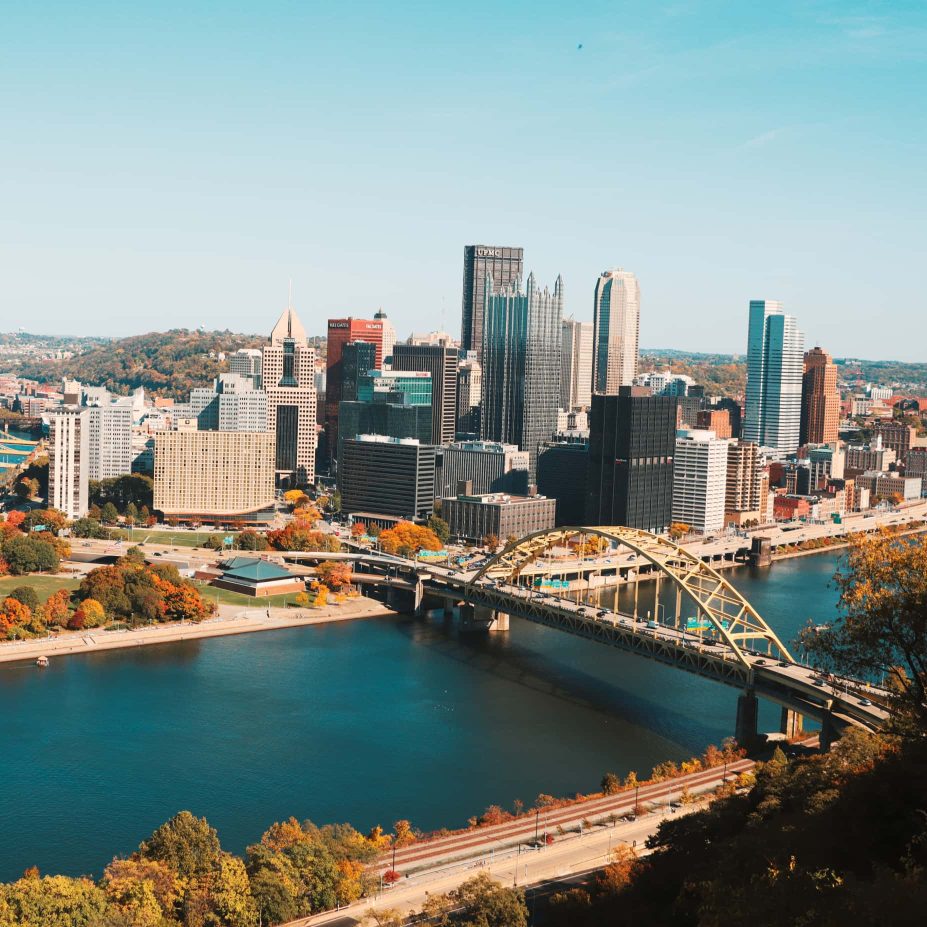

Traditional Work Ethic. Modern Execution. Since 1993.




We're shaping the future of AEC. Will you join us?
Keep up with Cadnetics news
Ready to Get to work?
Let Cadnetics be the extension of your team. Get the reliable, on-demand support and cutting-edge technology you need to stay under budget and ahead of schedule.